1. Models & Layers
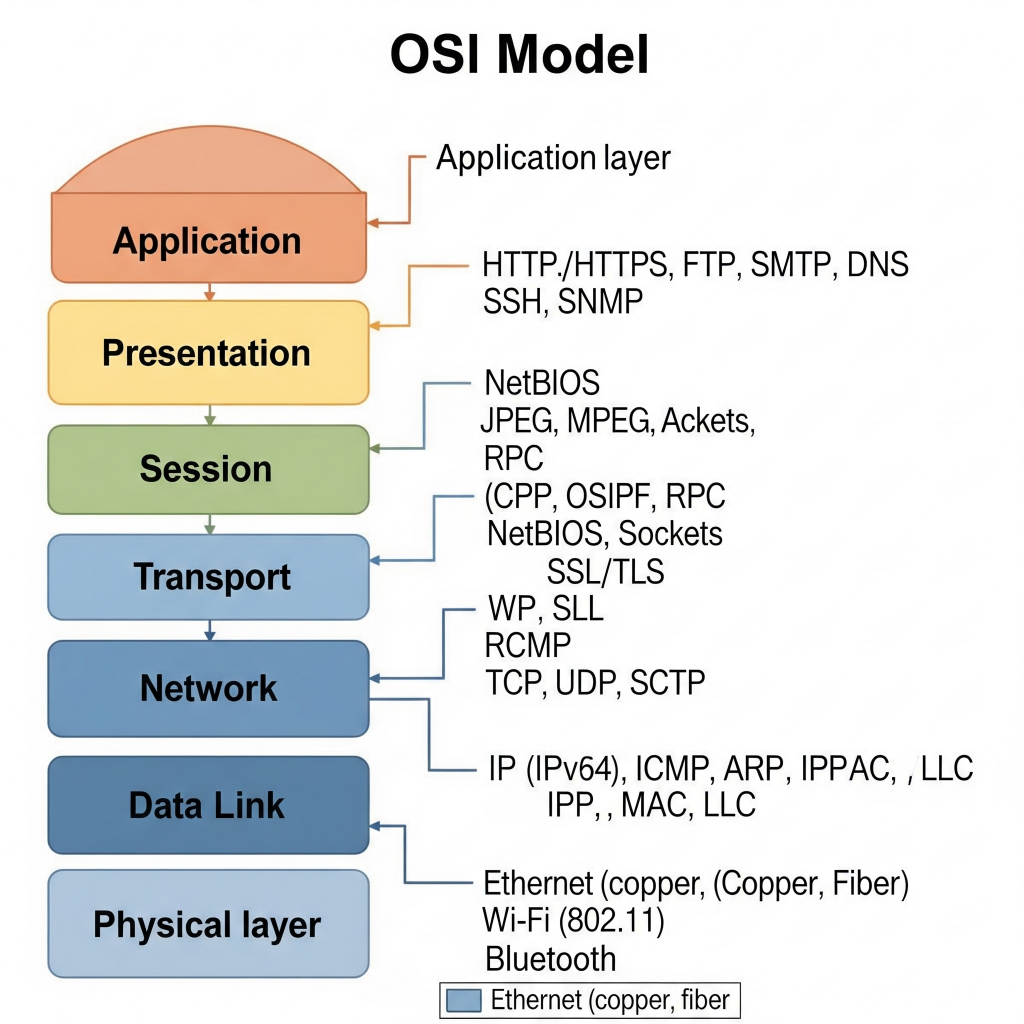
- OSI Model (7 layers → AP.ST.NDP)
👉 Application → Presentation → Session → Transport → Network → Data Link → Physical
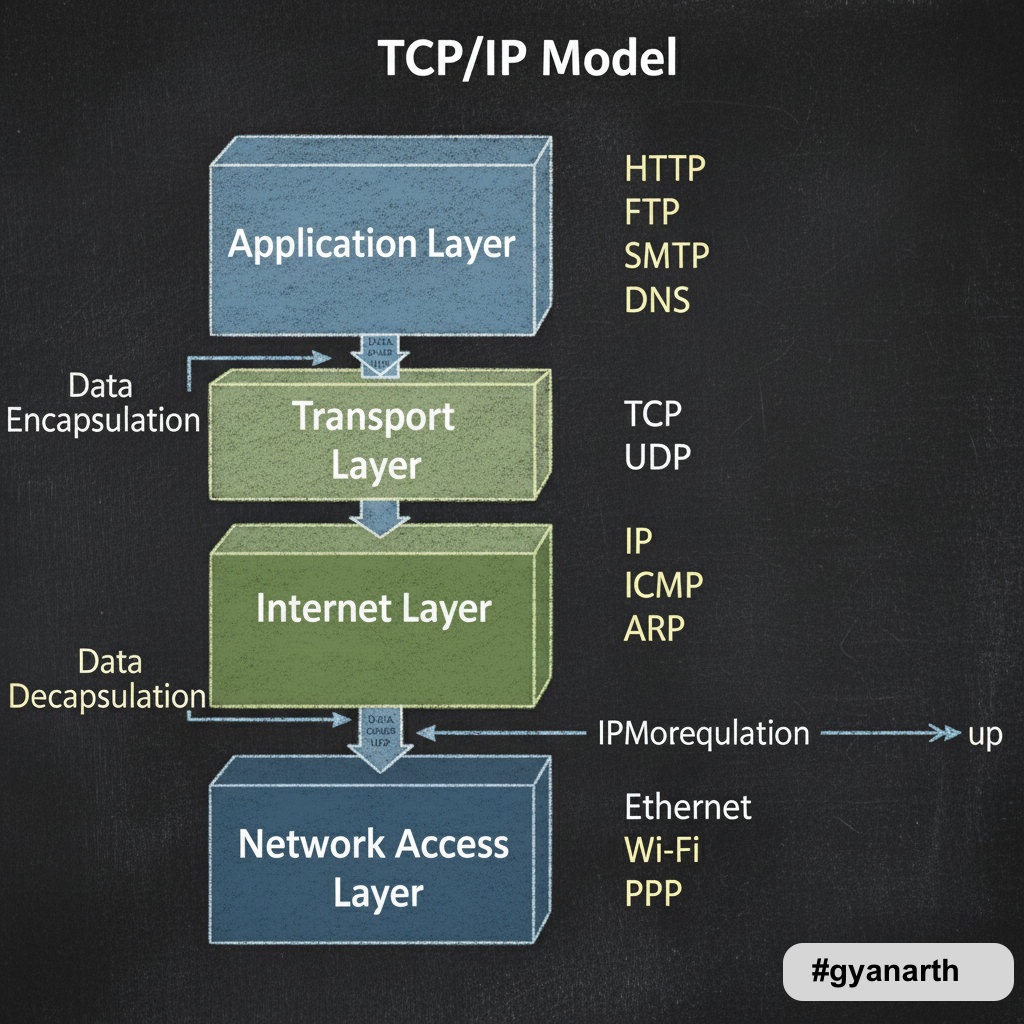
- TCP/IP Model (4 layers → AT.IN)
👉 Application → Transport → Internet → Network Access
2. Layers & Functions
1️⃣ Application Layer (OSI + TCP/IP)
What it does: User interaction, data generation, services.
Functions:
- Provides services to the user
- Runs software applications
- File transfer, email, browsing
Protocols:
HTTP/HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, POP3, IMAP, DNS, SNMP
Devices used:
- Application servers
- Web servers, Mail servers, DNS servers
- End-user devices (PC, mobile)
2️⃣ Presentation Layer (OSI)
Data formatting, encryption, compression
Functions:
- Encrypt / Decrypt
- Compress / Decompress
- Convert data formats (JPEG, PDF, MP3)
Devices used:
- No physical device (software layer)
- Used inside apps for encryption (e.g., SSL/TLS libraries)
3️⃣ Session Layer (OSI)
Start, manage, end communication (sessions)
Functions:
- Login session control
- Keep connection alive
- Synchronization
Devices used:
- No device (software-based)
- Used in session management tools & authentication systems
4️⃣ Transport Layer (OSI + TCP/IP)
Reliable/Unreliable delivery, segmentation, flow control.
Protocols:
- TCP → Reliable, connection-oriented
- UDP → Fast, no guarantee
Ports Examples:
80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), 21 (FTP), 25 (SMTP), 110 (POP3)
Devices used:
- Firewalls
- Load balancers
- Routers (for port forwarding)
5️⃣ Network Layer (OSI) / Internet Layer (TCP/IP)
Logical addressing & routing
Functions:
- Assign IP addresses
- Route packets between networks
Protocols:
IPv4, IPv6, ICMP, ARP, RARP, IGMP
🌍 IP Address & Routing
Devices:
- Router
- Layer 3 Switch
- Firewall (partly)
6️⃣ Data Link Layer (OSI) / Network Access Layer (TCP/IP)
MAC addressing, framing, error detection
Protocols:
Ethernet, PPP, Frame Relay, HDLC
🔐 MAC Address Layer → Local communication
Devices:
- Switch (Layer 2 switch)
- Bridge
- Access Points (Wi-Fi AP)
- NIC (Network Card)
7️⃣ Physical Layer (OSI)
Raw bits, electrical signals, physical connection
Functions:
- Cables, connectors
- Data transmission (0s and 1s)
🔌 Electricity & Hardware → Cables and Basic Devices
Devices:
- Cables (Ethernet, Fiber, Coax)
- Hub
- Repeater
- Connectors / Patch Panels
👉 Memory: “Physical = Things you can touch directly.”
3. Common Protocols & Ports
| Protocol | Port |
|---|---|
| FTP | 20, 21 |
| SSH | 22 |
| Telnet | 23 |
| SMTP | 25 |
| DNS | 53 |
| HTTP | 80 |
| HTTPS | 443 |
| SNMP –Simple Network Management Protocol is a tool used to monitor and manage network devices like routers, switches, and servers. | 161 |
| DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol automatically gives IP address to devices in a network. | 67, 68 |
🔑 Devices to Remember
📘 OSI Layers & Devices — Simplest Table
| Layer No. | Layer Name | Devices |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | Physical | Hub, Repeater, Cable, Modem – (HR-CM) |
| L2 | Data Link | Switch, Bridge, NIC, Access Point – (SB-NA) |
| L3 | Network | Router |
| L4 | Transport | Firewall, Load Balancer |
| L5 | Session | No Device |
| L6 | Presentation | No Device |
| L7 | Application | Gateway, Proxy, Application Firewall |
🎯 One-Line Quick Memory
L1 Hub
L2 Switch
L3 Router
L4 Firewall
L5 -
L6 -
L7 Gateway
🚀 MCQs ON NETWORK LAYERS, FUNCTIONS & PROTOCOLS
⭐ SECTION 1: OSI MODEL & LAYER-WISE FUNCTIONS
1. OSI model has how many layers?
A. 5
B. 6
C. 7
D. 8
✔ Ans: C
2. Which OSI layer provides end-to-end communication?
A. Network
B. Transport
C. Data Link
D. Session
✔ Ans: B
3. Which layer is responsible for routing?
A. Data Link layer
B. Network layer
C. Physical layer
D. Transport layer
✔ Ans: B
4. Which OSI layer is responsible for error detection and MAC addressing?
A. Data Link layer
B. Network layer
C. Session layer
D. Application layer
✔ Ans: A
5. Logical addressing (IP address) works at which layer?
A. Layer 1
B. Layer 2
C. Layer 3
D. Layer 4
✔ Ans: C
6. Physical addressing (MAC address) is at which layer?
A. Network
B. Data Link
C. Application
D. Transport
✔ Ans: B
7. The layer responsible for encryption and decryption is:
A. Session
B. Transport
C. Presentation
D. Application
✔ Ans: C
8. Which layer manages dialog control and sessions?
A. Presentation
B. Session
C. Data Link
D. Transport
✔ Ans: B
9. The topmost layer of OSI model is:
A. Transport
B. Presentation
C. Application
D. Network
✔ Ans: C
10. Data transmission format (syntax, compression) is handled by:
A. Application layer
B. Presentation layer
C. Data link layer
D. Physical layer
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 2: TCP/IP MODEL
11. TCP/IP model has ——— layers.
A. 5
B. 4
C. 6
D. 7
✔ Ans: B
12. Which layer does the Internet layer in TCP/IP correspond to?
A. Data Link
B. Network
C. Transport
D. Session
✔ Ans: B
13. SMTP works at which TCP/IP layer?
A. Application
B. Transport
C. Internet
D. Network Access
✔ Ans: A
14. The Transport layer protocols in TCP/IP are:
A. IP and ICMP
B. TCP and UDP
C. HTTP and FTP
D. ARP and RARP
✔ Ans: B
15. The TCP/IP layer responsible for framing and physical addressing:
A. Internet
B. Transport
C. Application
D. Network Access
✔ Ans: D
⭐ SECTION 3: IMPORTANT PROTOCOLS & THEIR LAYERS
16. HTTP, FTP, DNS belong to which layer?
A. Application
B. Transport
C. Network
D. Data Link
✔ Ans: A
17. Which protocol is connection-oriented?
A. UDP
B. TCP
C. IP
D. ARP
✔ Ans: B
18. Which protocol resolves IP address to MAC address?
A. DNS
B. DHCP
C. ARP
D. ICMP
✔ Ans: C – ARP is a protocol that finds the MAC address of a device when you only know its IP address.
19. ICMP is used for:
A. Email transfer
B. Error reporting and diagnostics
C. File transfer
D. Name resolution
✔ Ans: B – ICMP is a protocol used to send error messages and test network connectivity (like Ping).
20. Ping command uses:
A. HTTP
B. UDP
C. ICMP
D. RARP
✔ Ans: C
21. SMTP is used for:
A. Receiving emails
B. Sending emails
C. File transfer
D. Remote login
✔ Ans: B
22. POP3 and IMAP are used for:
A. Sending mail
B. Remote login
C. Receiving mail
D. DNS lookup
✔ Ans: C
23. FTP uses which ports?
A. 20 & 21
B. 23
C. 53
D. 80
✔ Ans: A
24. Telnet works on port:
A. 23
B. 21
C. 80
D. 53
✔ Ans: A
25. DNS uses which port?
A. 20
B. 23
C. 53
D. 110
✔ Ans: C
26. HTTPS uses port:
A. 80
B. 443
C. 21
D. 110
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 4: DATA LINK LAYER DETAILS
27. Switch operates at which layer?
A. Layer 1
B. Layer 2
C. Layer 3
D. Layer 7
✔ Ans: B
28. Router operates at:
A. Layer 2
B. Layer 3
C. Layer 4
D. Layer 7
✔ Ans: B
29. Frame Check Sequence (FCS) is used for:
A. Encryption
B. Error detection
C. Routing
D. Key exchange
✔ Ans: B – FCS is a value added at the end of a frame to detect errors during data transmission.
30. PPP and HDLC are protocols of:
A. Physical layer
B. Data Link layer
C. Network layer
D. Transport layer
✔ Ans: B – PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a WAN protocol used to connect two devices directly using serial links. HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control) is a WAN protocol used for reliable, bit-oriented communication over point-to-point links.
⭐ SECTION 5: IP ADDRESSING & NETWORK LAYER
31. IP is:
A. Connection-oriented
B. Connection-less
C. Reliable
D. Error-correcting
✔ Ans: B
32. Which protocol assigns IP addresses dynamically?
A. DNS
B. DHCP
C. FTP
D. ICMP
✔ Ans: B
33. Which protocol performs packet fragmentation?
A. ARP
B. IP
C. TCP
D. DHCP
✔ Ans: B
34. IPv6 address size is:
A. 32 bits
B. 64 bits
C. 128 bits
D. 256 bits
✔ Ans: C
35. Packet switching is performed at:
A. Application
B. Network
C. Data link
D. Transport
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 6: TRANSPORT LAYER
36. TCP provides:
A. Flow control
B. Congestion control
C. Reliability
D. All of the above
✔ Ans: D
37. UDP is used for:
A. File transfer
B. Video streaming
C. Secure communication
D. Email
✔ Ans: B
38. Port number size is:
A. 8 bits
B. 16 bits
C. 32 bits
D. 64 bits
✔ Ans: B
39. Segmentation occurs at:
A. Network layer
B. Transport layer
C. Data link layer
D. Physical layer
✔ Ans: B
40. Flow control is implemented using:
A. Checksum
B. Sliding window
C. TTL
D. Hop count
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 7: APPLICATION LAYER
41. Which protocol is used for remote login?
A. FTP
B. IMAP
C. Telnet
D. SMTP
✔ Ans: C
42. Which is a directory service protocol?
A. SMTP
B. LDAP
C. ICMP
D. POP
✔ Ans: B
43. Which is NOT an Application layer protocol?
A. HTTP
B. FTP
C. SMTP
D. ARP
✔ Ans: D
44. SNMP is used for:
A. Name resolution
B. Remote device monitoring
C. Email transfer
D. Routing
✔ Ans: B
45. DHCP uses: UDP or TCP?
A. TCP
B. UDP
C. Both
D. None
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 8: PHYSICAL LAYER
46. Which layer converts data into signals?
A. Transport
B. Presentation
C. Network
D. Physical
✔ Ans: D
47. Bit synchronization is done at:
A. Data link
B. Physical layer
C. Network layer
D. Session layer
✔ Ans: B
48. Hub operates at:
A. Layer 1
B. Layer 2
C. Layer 3
D. Layer 7
✔ Ans: A
⭐ SECTION 9: INTERNET PROTOCOL SUITE
49. Which protocol is used for network troubleshooting?
A. SNMP
B. ICMP
C. FTP
D. SMTP
✔ Ans: B – ICMP is a protocol used to send error messages and check network connectivity (like Ping).
50. Path MTU discovery uses:
A. TCP
B. ICMP
C. HTTPS
D. ARP
✔ Ans: B – Path MTU Discovery is a process that finds the largest packet size that can travel across a network path without breaking (fragmentation).
⭐ SECTION 10: MOST-EXPECTED Q
51. Three-way handshake is used by:
A. UDP
B. TCP
C. ICMP
D. DHCP
✔ Ans: B
52. Which layer ensures that packets reach the destination in order?
A. Data Link
B. Network
C. Transport
D. Session
✔ Ans: C
53. Which layer is responsible for QoS?
A. Network
B. Application
C. Transport
D. Data Link
✔ Ans: A
54. Which protocol resolves domain names to IP addresses?
A. FTP
B. DNS
C. DHCP
D. SNMP
✔ Ans: B
55. Which of the following is a routing protocol?
A. RIP
B. SMTP
C. FTP
D. DHCP
✔ Ans: A – RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a simple distance-vector routing protocol that chooses paths based on hop count.
